What is hip dysplasia?
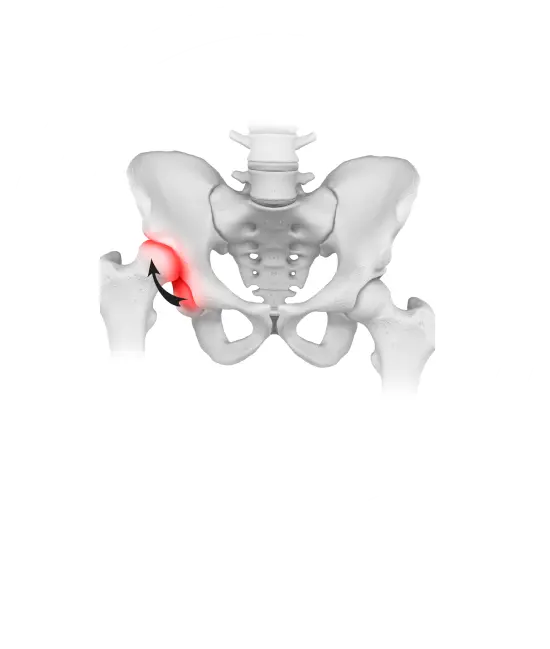
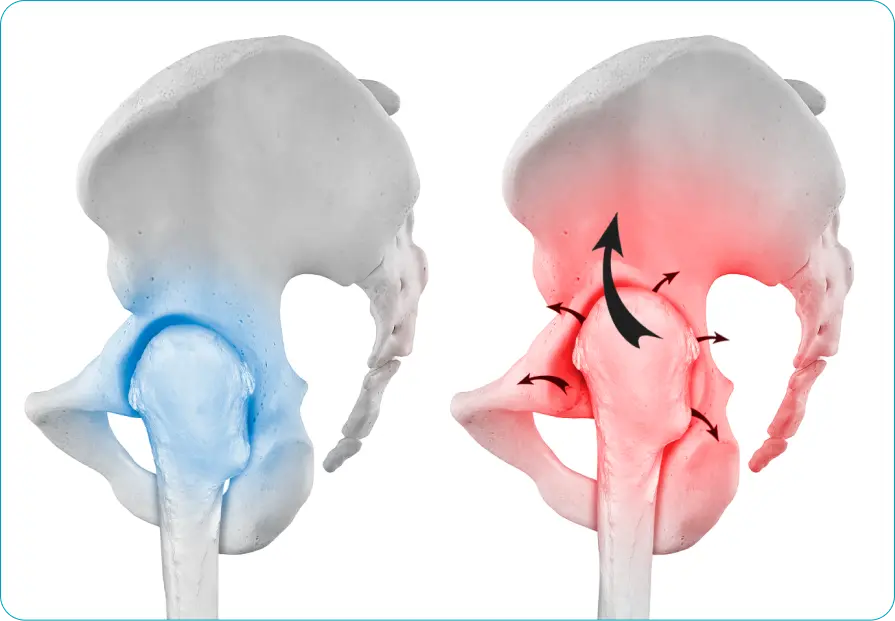
Dysplastic coxarthrosis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease due to congenital underdevelopment of the hip joint (hip dysplasia), in which deformation of the articular ends of the bones manifests itself in a change in the shape and depth of the acetabulum, a change in the cervical-diaphyseal angle and proximal femur.
Stages of hip dysplasia
According to the classification of J. Crowe, 4 stages of dysplasia are distinguished.
The first stage does not have pronounced clinical symptoms. The patient may complain of discomfort, minor aching pain. Movement restrictions are not observed at this stage. Radiographic images show a slight narrowing of the joint gap, as well as a slight subluxation of the head (less than 50%).
The second stage of the disease is characterized by increased pain, which can spread to the inguinal, popliteal region. Mobility is limited — flexion, extension, rotation of the limb is difficult. When moving, the patient can limp. Stage 2 dysplasia has more pronounced radiological changes — narrowing of the joint gap, change in the shape of the femoral head. Subluxation is more pronounced (displacement of the head by 50-75%).
They may have similar clinical symptoms. In the fourth stage of development of hip dysplasia, symptoms and limitation of movements are most pronounced. Pain is constantly present, sharply intensifies at the beginning of movement, bothers the patient more at night. The thigh muscles, pelvic muscles atrophy, the pelvis skews, one leg becomes shorter than the other. The patient wanders when walking — goose gait appears. X-ray shows a significantly deformed joint gap, changes in the bone structure of the femoral head, while with stage 3 dysplasia, the head displacement is 75-100%, and with stage 4, the head displaces by more than 100%. Left-sided, right-sided or bilateral dysplastic coxarthrosis of 3-4 stages leads to persistent impaired motor function and disability.
Development of hip dysplasia
The development of dysplasia is influenced by numerous and diverse abnormalities in the development of the bones of the pelvis, spine and lower extremities:
- Acetabulum reduction
- Congenital dislocations and subluxations
- Scoliosis of the spine
- Asymmetric growth
- Different length of lower extremities
The disease develops on the basis of Perthes disease, damage to one limb by poliomyelitis, hip fracture, injury to the head of the femur. Most often, hip dysplasia affects people of young, working age, mainly women. This disease is characterized not only by early manifestation, but also by a progressive course. This leads to a loss of ability to work and disability, a change in the entire way of life of a person, which makes the problem of treating this pathology not only medical, but also social.
Study
The study of etiopathogenesis of this disease made it possible to establish that the main factors contributing to its development are congenital progressive biomechanical imbalance and local overloads of chondral and subchondral joint structures.
The higher the degree of mechanical overloads associated with the underdevelopment of the mutually supporting zones of the femoral head and the acetabulum roof, the faster the breakdown of the resistant capabilities of the joint occurs.
Center staff
Treatment of hip dysplasia
is done by both conservative and surgical methods
Conservative treatment
It involves reducing weight, increasing physical activity and using crutches and canes. This allows you to slow down the progression of dysplasia and reduce the severity of symptoms. Also, the doctor can prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and chondoprotectors.
Surgical techniques
These include: endoprosthetics and organ-preserving operations (osteotomy, plastic surgery) for hip dysplasia
Difficulties in endoprosthetics are due to the complexity of preoperative planning; underdevelopment and deformation of bone elements of the joint, their mutual displacement, relative and absolute shortening of soft tissues, technical difficulties of the support itself associated with previous operations, the presence of scar tissues, the need to lower the femoral head, high trauma and duration of the operation, increased blood loss compared to standard endoprosthetics, a significant number of local intra- and postoperative complications.
Patient feedback

Don’t let joint pain define your life
Give yourself freedom of movement without restrictions
Over 5 years, using the DAA method, we returned more than 3 thousand patients to an active life.